Potential and kinetic energy worksheet answers
In this kinetic and potential energy worksheet article, first we will understand the fundamental concepts related to kinetic and potential energy. After that we will share some conceptual questions and worksheet PDF for your practice.
Kinetic Energy
In Physics, kinetic energy is very important concept. Kinetic energy is an energy, which is generated by motion of an object or a particle.
Let’s understand it in simple words. If we want to move an object, then we have to apply force on it. So, when we apply force, it requires some work to do. This work will transfer energy to the object. After that object will start moving.
Kinetic energy always depends on mass and velocity of the object. Kinetic energy is directly proportional to mass and velocity.
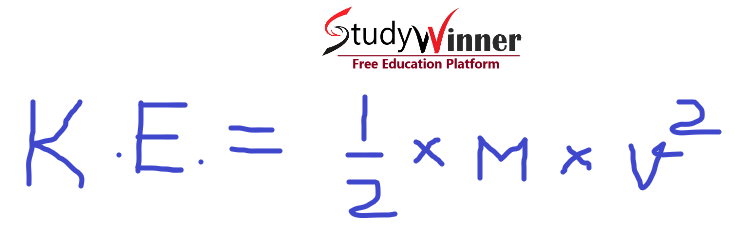
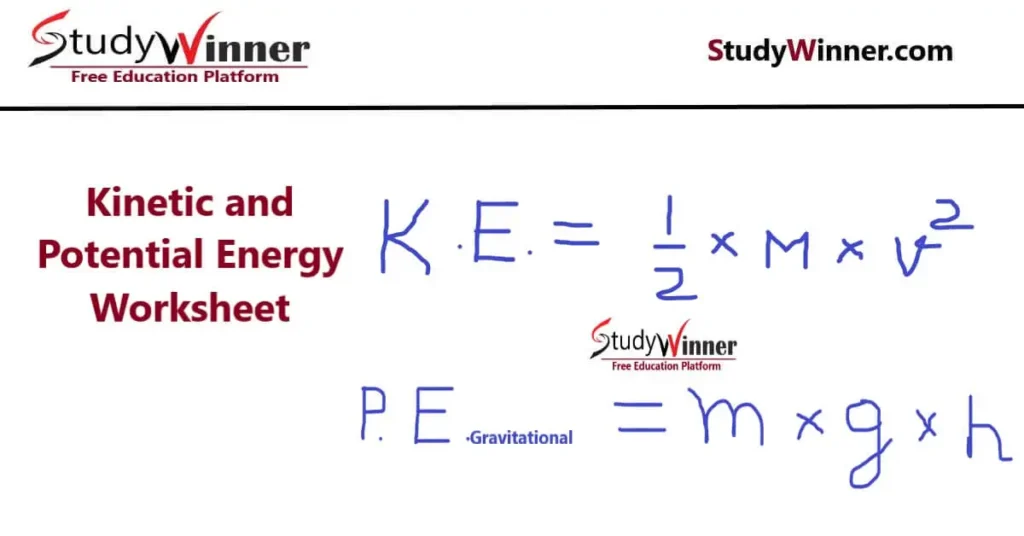
Where, K. E. = Kinetic Energy, M = Mass of an object, V = velocity of an object. Kinetic energy of an object always measured in Joules (J).
What are kinetic energy examples?
As we know that each and every moving object have Kinetic energy. Examples: Moving car, running person / athlete, swinging pendulum, flying birds, rolling ball etc.
- A car moving at a high speed possesses significant kinetic energy.
- A spinning top or a moving ball both exhibit kinetic energy.
- A person running or a cyclist in motion also have kinetic energy due to their movement.
Potential Energy
Potential energy is a stored energy because it’s held within the object itself. Gravitation potential energy is most common. We calculate gravitational potential energy based on the mass of the object (m), height of the object (h) and acceleration due to gravity (g).
Potential energy examples: Skydiver, stretched rubber band, compressed spring, battery and water in a dam.

Gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to the mass and height of the object.
When an object changes its state or start moving in any direction, potential energy converted into kinetic energy or work or any other form.
Download Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet PDF
| Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheet by www.thomas.k12.ga.us | Download |
| Solution of Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheet by www.thomas.k12.ga.us | Download |
| Kinetic VS Potential Energy Practice Sheet by www.scarsdaleschools.k12.ny.us | Download |
| Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet by www.wlwv.k12.or.us | Download |
| Potential and Kinetic Energy Sheet by www.auburn.wednet.edu | Download |
FAQs
A. Potential energy held within the object itself that’s why we call it stored energy. Gravitation potential energy is most common.
A. Kinetic energy is an energy, which is generated by motion of an object or a particle.
A. Kinetic Energy formula –
A. SI unit for energy is Joule (J).
A. Kinetic energy examples: Moving car, running person / athlete, swinging pendulum, flying birds, rolling ball etc.
Potential energy examples: Skydiver, stretched rubber band, compressed spring, battery and water in a dam.
A. SI unit for kinetic energy is Joule (J).
A. Gravitational potential energy formula –